Exhaust
11-3 Metered emissions test specifications
Applicable legislation
Application
Group M or N vehicles less than 20 years old (Note 4) and certified for entry on or after 1 May 2008 must pass a prescribed metered exhaust emissions test, according to the following procedures and requirements.
Note 1
This requirement does not apply to tractors, class MA or MC motorsport vehicles, or a vehicle certified to the low-volume vehicle standard exhaust gas emissions 90–10(00).
Note 2
This requirement does not apply to vehicles being re-registered or new vehicles.
Note 3
The entry inspector must personally carry out the tail-pipe test. Other staff may prepare the vehicle for testing but the test must be carried out by the entry inspector.
Note 4
Less than 20 years old means “a motor vehicle first registered outside of New Zealand, or manufactured, 20 years or less before its date of certification for entry into service”.
Procedure for measuring exhaust emissions of petrol, LPG or CNG vehicles
1. The test equipment must be warmed up and calibrated before use, in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Ensure the vehicle has reached normal operating temperature, as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
3. Insert the sampling probe (ie the exhaust gas sampling part of the measuring equipment) far enough into the exhaust pipe to prevent the admission of open air. This is to ensure that only exhaust gas is sampled.
4. For the duration of the test:
a) the vehicle’s engine must be idling, and
b) the acceleratior pedal must be released, and
c) the handbrake must be applied, and
d) the vehicle’s transmission must be
i. in neutral, or
ii. if the vehicle is an automatic, in park.
Pass requirements
A petrol, LPG or CNG vehicle must not exceed the applicable maximum carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions limits set out in below.
|
Vehicle |
Carbon monoxide |
Hydrocarbons |
|---|---|---|
|
A motor vehicle powered by a four-stroke or rotary engine |
1% |
300 |
|
A motor vehicle powered by a two-stroke engine |
4.5% |
7800 |
Re-testing
If a vehicle fails the test, it may be necessary to ensure the vehicle has reached normal operating temperature, as recommended by the manufacturer.
Procedure for measuring exhaust emissions of diesel vehicles (using an opacimeter)
Pre-testing
1. The vehicle must be brought to the normal operating temperature as recommended by the manufacturer.
2. The equipment must be readied before use, in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
During testing
For the duration of the test:
a) the vehicle must be stationary, and
b) the handbrake must be applied, and
c) the vehicle’s transmission must be:
i. in neutral, or
ii. if the vehicle is an automatic, in park.
Operation of the vehicle while testing
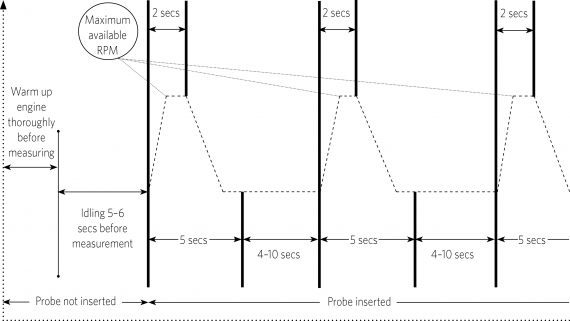
During the test procedure, the vehicle operation cycle must follow these phases (refer to Figure 11-3-1):
1. Purge
a) Residual smoke must be purged from the vehicle’s exhaust system before the vehicle’s diesel smoke is sampled.
2. Inserting probe
a) The probe (the exhaust gas sampling part of the measuring equipment) must be inserted sufficiently into the exhaust pipe to prevent outside air from entering the probe and ensure that only exhaust gas is sampled.
3. Idling before testing
a) The engine must be run at idle for five or six seconds before the first test cycle.
4. Test cycle
a) The accelerator pedal must be fully and rapidly depressed, held in this state for two seconds, then released for three seconds (refer to Figure 11-3-2).
b) Despite the above, if the opacimeter has a function allowing the measurement of the engine revloutions per minute (RPM), the accelerator pedal should only be depressed until the maximum available RPM is indicated by the opacimeter (rather than for the fixed period of two seconds).
c) The exhaust emissions must be sampled throughout this (five-second) period.
5. Idling between test cycles
a) The engine must be run at idle for 4–10 seconds between each test cycle that is performed.
Measured values
1. One, two or three test cycles must be performed as necessary.
a) If the result of measurement 1 is:
i. less than or equal to an optical absorption coefficient (OAC) of 0.64m-1, the vehicle passes the test,
ii. more than an OAC of 0.64m-1, the test cycle must be repeated.
b) If the result of measurement 2 is:
i. less than or equal to an OAC of 0.64m-1, the vehicle passes the test,
ii. more than 0.64m-1, the test cycle must be repeated.
c) If the average of the three measurements is:
i. less than or equal to an OAC of 0.80m-1, the vehicle passes the test,
ii more than an OAC of 0.80m-1, the vehicle fails the test.
2. To avoid doubt, if the vehicle does not meet the prescribed standard after three test cycles, the vehicle fails the test.
Figure 11-3-1. Diesel exhaust emission test vehicle operation cycle using an opacimeter
Procedure for measuring exhaust emissions of diesel vehicles (using filter paper test equipment)
Pre-testing
1. The test equipment must be warmed up and calibrated before use, in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Insert the sampling probe (ie the exhaust gas sampling part of the measuring equipment) far enough into the exhaust pipe to prevent the admission of open air. This is to ensure that only exhaust gas is sampled.
Operation of the vehicle during testing
For the duration of the test:
a) the vehicle must be stationary, and
b) the handbrake must be applied, and
c) the vehicle’s transmission must be:
i. in neutral, or
ii. if the vehicle is an automatic, in park.
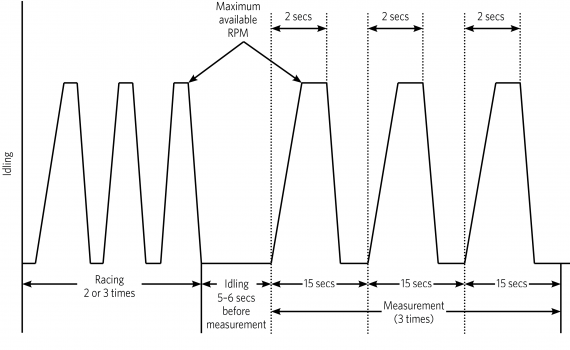
During the test procedure, the vehicle operation cycle must follow these phases (refer to Figure 11-3-2 over the page):
1. Racing purge
a) When the engine is idling, rapidly depress the accelerator to the maximum available RPM.
b) Immediately after the engine reaches its maximum available RPM, release the accelerator to return the engine to idling.
c) Repeat this two more times.
2. Idling phase
a) Run the engine at idle for five or six seconds.
3. Measuring phase
a) Fully depress the accelerator and hold for two seconds.
b) Release the accelerator for 13 seconds and sample the diesel smoke during this period.
c) Repeat this two more times.
Diesel sampling requirements
1. A sample of 0.33 litres must be absorbed through a filter paper by means of a pump-type exhaust smoke sampling device.
2. Class 5A filter paper (or equivalent) must be used.
3. The extent the filter paper is polluted by the smoke contained in the vehicle’s exhaust emissions must be measured by a prescribed exhaust smoke analyser measurement device.
4. The final result must be calculated as an average of the three measured values obtained during the test procedure.
Pass requirements
A diesel vehicle must not exceed 25% opacity.
Figure 11-3-2 Diesel exhaust emission test vehicle operation cycle
Page amended 1 January 2013 (see amendment details).