Correct as at 19th April 2024. It may be superseded at any time.
Extract taken from: Vehicle Inspection Portal > VIRMs > In-service certification (WoF and CoF) > Motorcycles > Miscellaneous items
13 Miscellaneous items
13-1 Engine and transmission
Reasons for rejection
Condition
1. An engine, gearbox, transfer case, differential or other driveline mounting is insecure.
2. A chain sprocket:
a) is loose, or
b) has excessively worn teeth.
3. A drive chain:
a) is excessively loose, or
b) has excessively worn links.
4. A driveshaft is bent or severely damaged.
5. A driveshaft flange:
a) is insecure, or
b) has a bolt or nut missing.
6. A rubber doughnut-type driveshaft coupling:
a) is worn or damaged beyond manufacturer’s specifications, or
b) is split or delaminated so that its mechanical integrity is affected, or
c) securing bolt is loose or missing.
7. A driveshaft universal joint spider (cross) bearing:
a) is worn so that the movement in the joint is beyond manufacturers specifications, or
b) caps have loose or missing cap bolts or circlips, or
c) is damaged, displaced or the seals between the spider journals and bearing caps are missing.
8. A driveshaft slip joint (spline) is worn beyond manufacturer’s specifications.
9. The universals in the driveshaft are not fitted in accordance with manufacturer’s specifications.
Modifications
10. A modification (Note 1) affects the engine and transmission, and:
a) is not excluded from the requirements for LVV specialist certification (Table 13-1-1), and
b) is missing proof of LVV specialist or accepted overseas certification, ie:
i. the vehicle is not fitted with a valid LVV certification plate, or
ii. the operator is not able to produce a valid modification declaration or authority card , or
iii. the vehicle has not been certified to an accepted overseas system as described in Technical bulletin 13.
Note 1 Definitions
Modify means to change a vehicle from its original state by altering, substituting, adding or removing a structure, system, component or equipment, but does not include repair.
Repair means to restore a damaged or worn vehicle, its structure, systems, components or equipment to within safe tolerance of its condition when manufactured, including replacement with undamaged or new structures, systems, components or equipment.
Note 2
LVV certification is always required for the fitting of a supercharger or turbocharger as a modification, or the upgrading of a supercharger, turbo or wastegate, or the re-chipping of electronic engine control units on turbo vehicles.
Table 13-1-1. Modifications that do not require LVV certification
Fitting of or modification to: | LVV certification is not required provided that: |
|---|---|
Substitution of engines |
– is of the same or less cubic capacity, and – has equal or less weight, and – has the same or less power output, and – uses the same fuel (petrol, diesel), and – uses the same unmodified attachment points, ie it bolts in, and – uses the same ancillary equipment (accelerator linkages etc). |
Minor modifications to OE engine |
– extractor or free-flow exhaust manifolds, or big bore exhaust systems – changed intake manifolds – changed or multiple carburettors – modified fuel injection systems – changed ignition systems – alternative cold air box induction systems.
|
Gearbox substitution |
|
Fitting of or modification to: | LVV certification is never required: |
|---|---|
Any modification for the purposes of law enforcement or the provision of emergency services |
|
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition and performance
1. The vehicle must be safe to be operated.
2. The components and materials must be fit for their purpose and within safe tolerance of their state when manufactured or modified.
Modifications
3. A modification that affects the engine and transmission must be inspected and certified by an LVV specialist certifier, unless the vehicle:
a) is excluded from the requirement for LVV specialist certification (Table 13-1-1), and
b) has been inspected in accordance with the requirements in this manual, including those for equipment, condition and performance.
Page amended 1 April 2024 (see amendment details).
13-2 Fuel system
Reasons for rejection
Condition
1. There is a noticeable fuel leak from the fuel system.
2. There is corrosion damage (Note 1), cracking or other damage within 150mm of a tank mounting.
3. The security of the fuel tank is affected by insecure or loose tank mountings.
4. A fuel line is insecure or loose so that it is likely to be damaged during normal use of the vehicle.
5. A fuel pipe is severely damaged or excessively corroded.
6. A fuel hose is damaged or perished.
7. The fuel pump is insecure.
8. The fuel filler cap or capless fuel filler seal is missing, insecure, or likely to allow fuel spillage when the vehicle is in normal use.
9. The fuel tank is fitted with a ‘temporary use’ fuel filler cap.
Modification
10. A modification (Note 1) affects the fuel system, and:
a) is not excluded from the requirements for LVV specialist certification (Table 13-2-1), or
b) is missing proof of LVV specialist or accepted overseas certification, ie:
i. the vehicle is not fitted with a valid LVV certification plate, or
ii. the operator is not able to produce a valid modification declaration or authority card , or
iii. the vehicle has not been certified to an accepted overseas system as described in Technical bulletin 13 .
Note 1 Definitions
Corrosion damage is where the metal has been eaten away, which is evident by pitting. The outward signs of such corrosion damage is typically displayed by the lifting or bubbling of paint. In extreme cases the area affected by corrosion damage will fall out and leave a hole.
Modify means to change a vehicle from its original state by altering, substituting, adding or removing a structure, system, component or equipment, but does not include repair.
Repair means to restore a damaged or worn vehicle, its structure, systems, components or equipment to within safe tolerance of its condition when manufactured, including replacement with undamaged or new structures, systems, components or equipment.
Table 13-2-1. Modifications that do not require LVV certification
Fitting of or modification to: | LVV certification is not required provided that: |
|---|---|
Fuel system changes and modifications |
|
Fitting of or modification to: | LVV certification is never required: |
|---|---|
Any modification for the purposes of law enforcement or the provision of emergency services |
|
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition and performance
1. Fuel tanks, fuel lines and associated components must be:
a) securely mounted, and
b) made of suitable materials, and
c) in good condition, and
d) free from significant leaks, and
e) positioned so that the risk of mechanical damage or heat gain is minimised.
Modification
2. A modification that affects the fuel tank and fuel lines must be inspected and certified by a low volume vehicle specialist certifier, unless the vehicle:
a) is excluded from the requirement for LVV certification (Table 13-2-1), and
b) has been inspected in accordance with the requirements in this manual, including those for equipment, condition and performance.
Page amended 1 December 2016 (see amendment details).
13-5 Electric and hybrid vehicle electrical system
Reasons for rejection
Condition (Note 1)
1. High voltage wiring is:
a) insecure or not adequately secured
b) damaged or deteriorated (including insulation)
c) likely to touch:
i. hot components of the vehicle
ii. sharp edges
iii. rotating parts
iv. the ground.
2. High voltage batteries are:
a) insecure or not adequately secured
b) damaged or deteriorated (including components and electrical insulation)
c) leaking, or showing signs of leaking.
3. High voltage battery shields are damaged or not in place.
Modification
4. A modification affects the electrical system, and:
a) is not excluded from the requirements for specialist certification (Table 13-5-1), or
b) is missing proof of specialist certification, that is:
i. the vehicle is not fitted with a valid certification plate (eg low volume vehicle plate or heavy vehicle certification plate/label), or
ii. the operator is not able to produce a valid modification declaration or authority card
iii. The vehicle has not been certified to an accepted overseas system as described in Technical bulletin 13.
Note 1
Vehicle inspectors are only required to do a visual check. An invasive check is not required.
Table 13-5-1. Modifications that do not require specialist certification
Fitting of or modification to: | Specialist certification is not required provided that: |
|---|---|
Fuel system changes and modifications |
Note: Specialist certification is always required for changes to the high voltage electrical system. |
Fitting of or modification to: | Specialist certification is never required: |
|---|---|
Any modification for the purposes of law enforcement or the provision of emergency services |
|
Table 13-5-2. Electrical system warning icons
General fault The vehicle may indicate exactly what the fault is. If the fault is not from an electrical system, or other safety critical system (eg brakes, steering, electrics, ESC etc.) the vehicle may pass the inspection. |  |
Vehicle electrical fault The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. If the fault is not from a safety critical system (eg brakes, steering, high voltage electrics, ESC etc.), the vehicle may pass the inspection. |  |
Limited power/Limp mode This is likely to do with a fault in the electric drive system. The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. |  |
Serious electrical fault The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. | 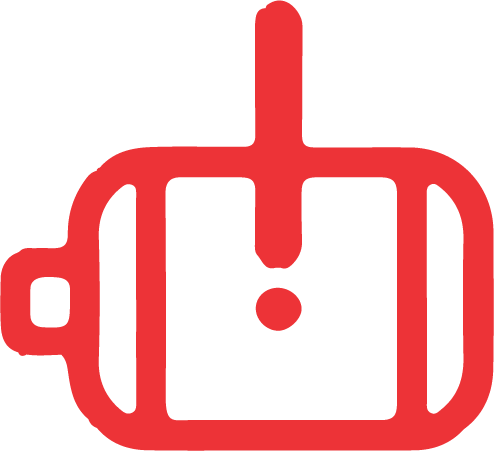 |
Master warning Could be a warning for any vehicle system and is likely to be serious. The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. |  |
High battery temperature Remove the car from any indoor premises immediately and turn the vehicle off. The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. | 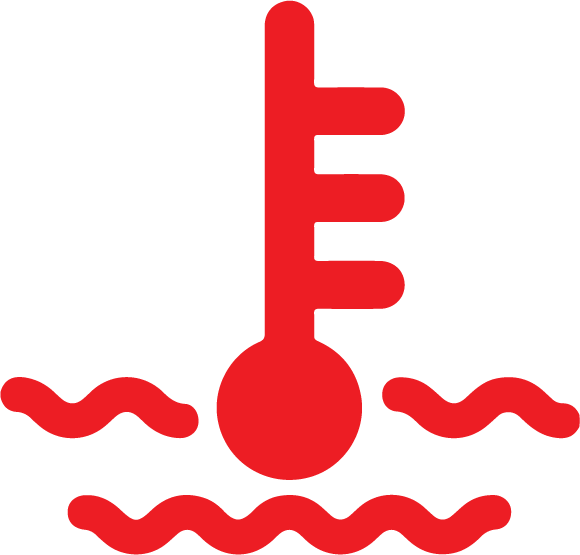 |
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition and performance
1. The vehicle must be safe to be operated.
2. The components and materials must be fit for their purpose and within safe tolerance of their state when manufactured or modified.
Modifications
3. A modification that affects the electrical system must be inspected and certified by an specialist certifier, unless the vehicle:
a) is excluded from the requirement for specialist certification (Table 13-5-1), and
b) has been inspected in accordance with the requirements in this manual, including those for equipment, condition and performance.
Page amended 1 October 2021 (see amendment details).