Correct as at 23rd April 2024. It may be superseded at any time.
Extract taken from: Vehicle Inspection Portal > VIRMs > Light vehicle repair certification > Motorcycles
10 Motorcycles
10-1 Frames and forks
Reasons for rejection
1. A motorcycle frame has not been replaced when there is evidence that it had been deformed so that a localised kink of 90° or more has been formed over a small radius.
2. A motorcycle frame has been heated.
3. A steel frame of a motorcycle has been sectioned without an insert.
4. Heat has been applied to a frame in a manner that is not permitted in the manufacturer’s instructions.
5. A frame has been heated as part of the repair and the manufacturer’s temperatures and time limits have not been followed or evidence that this process has been followed has not been presented with the LT308 (Note 2).
6. A fork has been heated.
7. A fork has been straightened but the cross section has been deformed.
8. A thin-walled fork has been straightened after being bent more than 15°.
9. A fork has been straightened when the original damage is not known.
10. A fork has been sectioned.
Note 1
Damaged parts should be replaced at factory seams whenever practicable and when required by the vehicle manufacturer.
Note 2
If a frame is heated as part of a repair, evidence of the process must be included with the LT308. This should include such information as the manufacturer’s specifications, temperature indicator used and the time that the heat was applied for.
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition
1. A repair to a vehicle, its structure, systems, components or equipment must restore the damaged or worn vehicle, structure, system, component or equipment so that it is within safe tolerance of the state of the vehicle, structure, system, component or equipment when manufactured.
10-2 Measurements
Reasons for rejection
1. A fork has runout in excess of 0.4mm (unless permitted by the manufacturer).
2. One of the following measurements is not within the manufacturer’s specifications:
a) wheelbase (Figure 10-2-1)
b) steering head angle (Figure 10-2-2)
c) front wheel castor angle (Figure 10-2-3)
d) wheel track offset (Figure 10-2-4).
3. The wheel alignment has not been measured.
4. The wheel alignment is not within specification.
5. A reference measurement of the frame has not been completed and recorded (Note 1).
6. A reference measurement of the frame shows a difference of more than 3mm (unless permitted by the manufacturer’s instructions).
Note 1
A reference measurement of the frame is a comparative measurement of each side of the frame to verify symmetry.
Figure 10-2-1. Wheelbase measurement
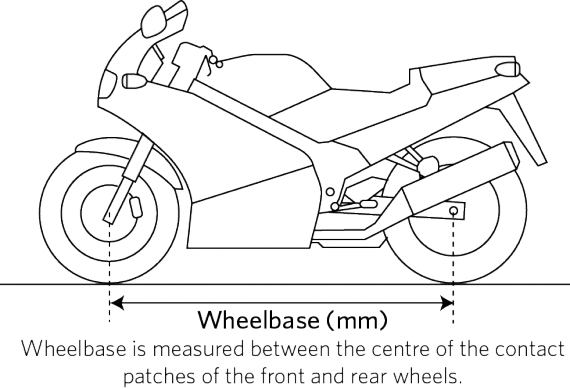
Figure 10-2-2. Steering head angle measurement
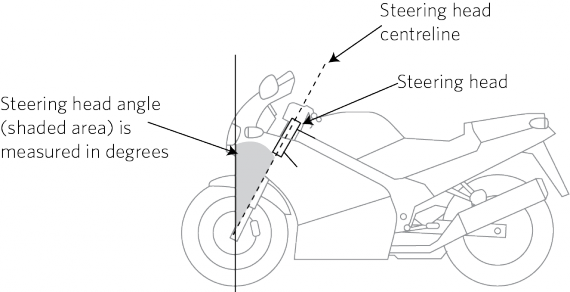
Figure 10-2-3. Front wheel castor angle measurement
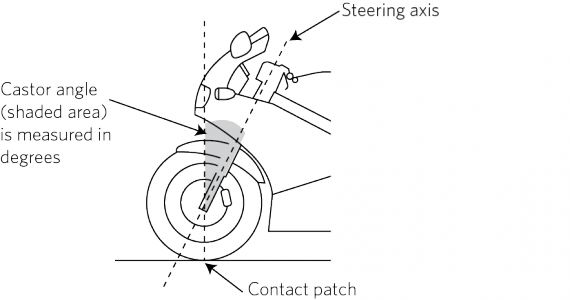
Figure 10-2-4. Wheel track offset measurement
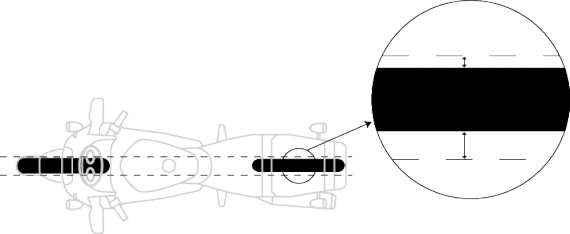
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition
1. A repair to a vehicle, its structure, systems, components or equipment must restore the damaged or worn vehicle, structure, system, component or equipment so that it is within safe tolerance of the state of the vehicle, structure, system, component or equipment when manufactured.