Correct as at 26th April 2024. It may be superseded at any time.
Extract taken from: Vehicle Inspection Portal > VIRMs > Entry certification > Inspection and certification > Exhaust
11 Exhaust
11-1 Exhaust system and silencer
Reasons for rejection
Mandatory equipment
1. A vehicle does not comply with the requirements relating to mandatory equipment set out in:
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, general vehicles
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, heavy vehicles
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, light PSVs
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, heavy PSVs.
Compliance with approved standards
2. A class LC, LD, LE, MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC vehicle, other than one listed in Table 11-1-1, manufactured on or after 1 January 1985 and certified for entry on or after 1 June 2008:
a) did not comply, or cannot be demonstrated to have complied, with at least one of the approved standards listed in Table 11-1-2 at the time the vehicle was manufactured, or
b) exceeded the noise limits in Table 11-1-2 when it was tested in accordance with the standards in Table 11-1-2 at the time the vehicle was manufactured, or
c) does not have evidence that the vehicle has passed an LVVTA objective noise test, for instance:
i. the owner cannot produce a valid ‘Objective exhaust noise emission test certificate’ (Figure 11-1-1), or
ii. the exhaust system tailpipe is not fitted with a valid LVVTA noise test label (Figure 11-1-2).
Condition and performance
3. A vehicle does not comply with the requirements relating to condition and performance set out in:
Table 11-1-1. Vehicles deemed to comply with approved noise standards and drive-by noise limits
|
Evidence of compliance with an approved noise standard and noise limit is not required for the following vehicles: |
|---|
|
Table 11-1-2. List of approved noise standards and drive-by noise limits
|
A vehicle manufactured on or after 1985 for which evidence of compliance with an approved standard and noise level is required must comply with the following: |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Approved noise standard |
Vehicle class |
Maximum noise level (dBA) |
|
ISO 362 BS 3425 SAE J1470 ADR 28/01 TRIAS 20 |
LC, LD, LE (engine capacity of 125 cc or less) LC, LD, LE (engine capacity more than 125 cc) MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, NA MD3, MD4, ME, NB, NC (power output 150 kW or less) MD3, MD4, ME, NB, NC (power output more than 150 kW) |
82 86 81 86 88 |
Figure 11-1-1. Objective exhaust noise emission test certificate
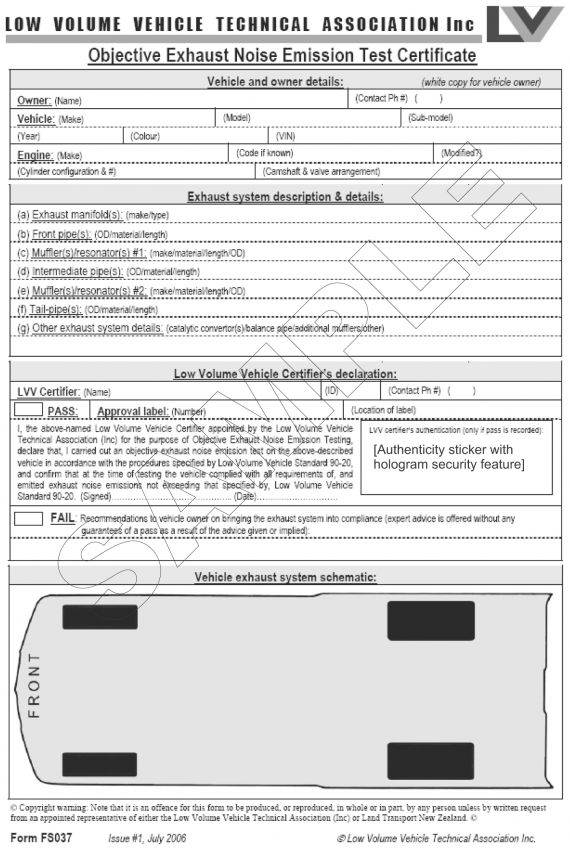
Figure 11-1-2. Objective noise test label

Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Mandatory equipment
1. A vehicle must comply with the requirements relating to mandatory equipment set out in:
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, general vehicles
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, heavy vehicles
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, light PSVs
- VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1, heavy PSVs.
Compliance with approved standards
2. A class LC, LD, LE, MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC vehicle manufactured on or after 1 January 1985 and certified for entry on or after 1 June 2008 must comply with:
a) an approved standard and not exceed the relevant noise limit, as specified in Table 11-1-2, or
b) the LVVTA objective noise test.
Condition and performance
3. The exhaust system and silencer must comply with the requirements relating to condition and performance set out in the relevant section of the VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-1.
Modification
4. A vehicle must comply with the requirements relating to modifications set out in:
11-2 Exhaust emissions
Reasons for rejection
Compliance with approved standards
1. A vehicle that is required to comply with an approved exhaust emission standard did not comply or cannot be demonstrated to have complied with at least one of the standards listed in the following tables at the time the vehicle was manufactured:
- Table 11-2-1. Approved exhaust emission standards for used vehicles certified for use on New Zealand roads before 3 January 2008
- Table 11-2-2. Approved exhaust emission standards for used petrol-, CNG- and LPG-powered vehicles certified for use on New Zealand roads on or after 3 January 2008
- Table 11-2-3. Approved exhaust emission standards for used diesel-powered vehicles certified for use on New Zealand roads on or after 3 January 2008
- Table 11-2-4. Approved exhaust emission standards for new petrol-, CNG- and LPG-powered vehicles
- Table 11-2-5. Approved exhaust emission standards for new diesel-powered vehicles.
Performance and modification
2. A class MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC vehicle does not pass the prescribed metered emissions test (see section 11-3, Metered emissions test specifications).
3. The exhaust system does not comply with requirements relating to performance set out in the VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-2.
Note 1
A transitional provision of the Rule allows vehicles border checked for entry into New Zealand before 1 Febuary 2008 to meet earlier requirements, as set out in Table 11-2-1.
Note 2
Technical bulletin 28 describes methods of proving compliance with approved emissions standards, and explains how to record the information in LANDATA.
Note 3
The Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Exhaust Emissions does not apply to ancillary engines that do not power the vehicle’s wheels.
Note 4
The following vehicles are not required to meet an emissions standard:
- Tractors (for the purpose of the Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Exhaust Emissions, a tractor means a motor vehicle, other than a traction engine, constructed principally for towing an agricultural trailer or for powering agricultural implements)
- Class L vehicles
- Class MA or MC motorsport vehicle
- Class MA special interest vehicles
- Immigrants’ vehicles
- Mobile cranes
- Low volume production vehicles that comply with the emissions requirements of the Low Volume Vehicle Code.
Note 5
Reference material 61 describes the option to repower a heavy vehicle to meet emission requirements.
Note 6
A vehicle more than 20 years old is not required to comply with an exhaust emission standard or have a metered tailpipe test.
Table 11-2-1. Approved exhaust emission standards for used vehicles certified for use on New Zealand roads before 3 January 2008
Petrol-powered vehicles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
UN-ECE Regulation No. | EEC/EC Directive | ADR | Japan | Others |
15 | 70/220 | 36 | Japan Safety Regulations for Road Vehicles, Article 31 | Federal Regulation 40 CFR Part 86 Title 13 of the California Code of Regulations Mean Value Standards for Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions, No. 129 |
Diesel-powered vehicles | ||||
UN-ECE Regulation No. | EEC/EC Directive | ADR | Others | |
24 | 72/306 | ADR 30 | Federal Regulation 40 CFR Part 86 Title 13 of the California Code of Regulations The Mean Value Standards for Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions, No. 129 | |
Low volume vehicles | ||||
As defined in the Low Volume Vehicle Code | ||||
Table 11-2-2. Approved exhaust emission standards for used petrol-, CNG- and LPG-powered vehicles certified for use on New Zealand roads on or after 3 January 2008
Certified for entry into service | Approved vehicle emissions standards | |
|---|---|---|
| Light vehicles | Heavy vehicles | |
On or after 1 January 2012 (Note 7) | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/02, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 |
Note 7
A transitional provision of Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Exhaust Emissions 2007 allows vehicles border checked for entry into New Zealand before 1 February 2008 to meet earlier requirements (as set out in Table 11-2-1).
Note 8
Under a transitional provision of Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Exhaust Emissions 2007, a vehicle that complied with the Japan 98 Idling Standard when it was manufactured or modified and has a Japanese emissions code of GF, HK, GG, or HL is deemed to have complied with Japan 98.
Table 11-2-3. Approved exhaust emission standards for used diesel-powered vehicles certified for use on New Zealand roads on or after 3 January 2008
Certified for entry into service | Approved vehicle emissions standards | |
|---|---|---|
| Light vehicles | Heavy vehicles | |
On or after 1 January 2010 | ADR 30/01 and ADR 79/01, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 30/01 and ADR 80/02, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 |
Note 9
A transitional provision of Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Exhaust Emissions allows vehicles border checked for entry into New Zealand before 1 February 2008 to meet earlier requirements (as set out in Table 11-2-1).
Table 11-2-4. Approved exhaust emission standards for new petrol-, CNG- and LPG-powered vehicles
Date of manufacture | Approved vehicle emissions standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Light | Heavy | |||
New model | Existing model | New model | Existing model | |
Before 3 January 2008 | ADR 79/01, or Euro 3, or Japan 00/02, or US 2001 | ADR 79/01, or Euro 3, or Japan 00/02, or US 2001 | ADR 80/01, or Japan 00/02, or US 98P | ADR 80/01, or Japan 00/02, or US 98P |
On or after 3 January 2008 and before 1 January 2009 | Before 1 July 2008 On or after 1 July 2008 Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 79/01, or Euro 3, or Japan 00/02, or US 2001 | ADR 80/02, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/02, Euro IV, or Japan 00/02, or US 98P |
On or after 1 January 2009 and before 1 January 2010 | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 79/01, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/02, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/02, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 |
On or after 1 January 2010 and before 1 January 2011 | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | Before 1 July 2010 On or after 1 July 2010 Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/02, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 |
On or after 1 January 2011 and before 1 January 2012 | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, or Euro V, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, or Euro IV, or Japan 05, or US 2004 |
On or after 1 January 2012 and before 1 November 2013 | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 79/02, or Euro 4, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, or Euro V, or Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, or Euro V, or Japan 05, or US 2004 |
On or after 1 November 2013 and before 1 January 2014 | ADR 79/03, Euro 5, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 79/02, Euro 4, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2004 |
| On or after 1 January 2014 and before 1 January 2015 | ADR 79/03, Euro 5, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 79/02, Euro 4, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2004 |
| On or after 1 January 2015 and before 1 November 2016 | ADR 79/03, Euro 5, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 79/02, Euro 4, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 |
| On or after 1 November 2016 | ADR 79/04, Euro 5, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 79/04, Euro 5, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05; Japan 09, or US 2007 |
Notes to Table 11-2-4 and Table 11-2-5
1. New-model vehicle means a new motor vehicle that has a date of manufacture occurring in the same calendar year as that in which the particular model of the vehicle was first manufactured.
2. Existing-model vehicle means a new vehicle that is not a new-model vehicle.
3. To help confirm emissions standards compliance, see Technical bulletin 28 – Exhaust emissions standards compliance.
4. To help confirm emissions standards compliance for new heavy vehicles imported by the manufacturer’s New Zealand representative, refer to Reference material 43.
Table 11-2-5. Approved exhaust emission standards for new diesel-powered vehicles
Date of manufacture | Approved vehicle emissions standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Light | Heavy | |||
New model | Existing model | New model | Existing model | |
Before 3 January 2008 | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 80/00 and ADR | ADR 80/00 and ADR |
On or after 3 January 2008 and before 1 January 2009 | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 80/02 and ADR | ADR 80/00 and ADR |
On or after 1 January 2009 and before 1 January 2010 | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 80/02 and ADR | ADR 80/02 and ADR |
On or after 1 January 2010 and before 1 January 2011 | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 80/03, or | ADR 80/02 and ADR |
On or after 1 January 2011 and before 1 January 2012 | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 80/03, or | ADR 80/02, or |
On or after 1 January 2012 and before 1 November 2013 | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 79/01 and ADR | ADR 80/03, or | ADR 80/02, or |
| On or after 1 November 2013 and before 1 January 2014 | ADR 79/03, Euro 5, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 79/01 and ADR 30/01, Euro 4, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2004 |
| On or after 1 January 2014 and before 1 January 2015 | ADR 79/03, Euro 5, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 79/01 and ADR 30/01, Euro 4, Japan 05, or US 2004 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 09, or US 2007 | Manufactured before 1 July 2014 ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2004. Manufactured on or after 1 July 2014 ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 05, or US 2007 |
| On or after 1 January 2015 and before 1 November 2016 | ADR 79/03, Euro 5, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 79/01 and ADR 30/01, Euro 4, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 09, or US 2007 |
| On or after 1 November 2016 | ADR 79/04, Euro 5, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 79/04, Euro 5, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 09, or US 2007 | ADR 80/03, Euro V, Japan 09, or US 2007” |
Notes to Table 11-2-4 and Table 11-2-5
1. New-model vehicle means a new motor vehicle that has a date of manufacture occurring in the same calendar year as that in which the particular model of the vehicle was first manufactured.
2. Existing-model vehicle means a new vehicle that is not a new-model vehicle.
3. To help confirm emissions standards compliance, see Technical bulletin 28 – Exhaust emissions standards compliance.
4. To help confirm emissions standards compliance for new heavy vehicles imported by the manufacturer’s New Zealand representative, refer to Reference material 43.
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Compliance with approved standards
1. A used vehicle of class MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC, less than 20 years old and:
a) certified for entry into New Zealand before 3 January 2008 must comply with one or more of the approved exhaust emission standards in Table 11-2-1
b) powered by petrol, CNG or LPG and border checked for entry into New Zealand on or after 3 January 2008 must comply with one or more of the approved exhaust emission standards in Table 11-2-2 (Note 1)
c) powered by diesel and border checked for entry into New Zealand on or after 3 January 2008 must comply with one or more of the approved exhaust emission standards in Table 11-2-3 (Note 1).
2. New petrol, CNG or LPG powered vehicles of class MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC, less than 20 years old must comply with one or more of the approved exhaust emission standards in Table 11-2-4.
3. New diesel-powered vehicles of class MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC, less than 20 years old must comply with one or more of the approved exhaust emission standards in Table 11-2-5.
4. The following vehicles are not required to meet an emissions standard:
- Class MA or MC motorsport vehicle
- Class MA special interest vehicles
- Immigrants’ vehicles
- Mobile cranes (does not include a truck mounted with crane apparatus)
- Low volume scratchbuilt and modified production vehicles that comply with the emissions requirements of the Low Volume Vehicle Code.
5. A vehicle more than 20 years old is not required to comply with an exhaust emission standard
6.The Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Exhaust Emissions does not apply to ancillary engines that do not power the vehicle’s wheels. eg refrigeration units, motorhome electricity generators
7. A vehicle used exclusively by the New Zealand Defence Force may be fitted with a defeat device to override an exhaust emissions control on the vehicle
Performance
8. Class MA, MB, MC, MD1, MD2, MD3, MD4, ME, NA, NB or NC vehicles manufactured on or after 1 January 1990 and first certified for entry into New Zealand on or after 1 May 2008 must pass a prescribed metered test (see section 11-3, Metered test specifications).
9. The exhaust system must comply with requirements relating to performance set out in the VIRM: In-service certification, section 11-2.
Page amended 2 December 2019 (see amendment details).
11-3 Metered emissions test specifications
Applicable legislation
Application
Group M or N vehicles less than 20 years old (Note 4) and certified for entry on or after 1 May 2008 must pass a prescribed metered exhaust emissions test, according to the following procedures and requirements.
Note 1
This requirement does not apply to tractors, class MA or MC motorsport vehicles, or a vehicle certified to the low-volume vehicle standard exhaust gas emissions 90–10(00).
Note 2
This requirement does not apply to vehicles being re-registered or new vehicles.
Note 3
The entry inspector must personally carry out the tail-pipe test. Other staff may prepare the vehicle for testing but the test must be carried out by the entry inspector.
Note 4
Less than 20 years old means “a motor vehicle first registered outside of New Zealand, or manufactured, 20 years or less before its date of certification for entry into service”.
Procedure for measuring exhaust emissions of petrol, LPG or CNG vehicles
1. The test equipment must be warmed up and calibrated before use, in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Ensure the vehicle has reached normal operating temperature, as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
3. Insert the sampling probe (ie the exhaust gas sampling part of the measuring equipment) far enough into the exhaust pipe to prevent the admission of open air. This is to ensure that only exhaust gas is sampled.
4. For the duration of the test:
a) the vehicle’s engine must be idling, and
b) the acceleratior pedal must be released, and
c) the handbrake must be applied, and
d) the vehicle’s transmission must be
i. in neutral, or
ii. if the vehicle is an automatic, in park.
Pass requirements
A petrol, LPG or CNG vehicle must not exceed the applicable maximum carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions limits set out in below.
|
Vehicle |
Carbon monoxide |
Hydrocarbons |
|---|---|---|
|
A motor vehicle powered by a four-stroke or rotary engine |
1% |
300 |
|
A motor vehicle powered by a two-stroke engine |
4.5% |
7800 |
Re-testing
If a vehicle fails the test, it may be necessary to ensure the vehicle has reached normal operating temperature, as recommended by the manufacturer.
Procedure for measuring exhaust emissions of diesel vehicles (using an opacimeter)
Pre-testing
1. The vehicle must be brought to the normal operating temperature as recommended by the manufacturer.
2. The equipment must be readied before use, in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
During testing
For the duration of the test:
a) the vehicle must be stationary, and
b) the handbrake must be applied, and
c) the vehicle’s transmission must be:
i. in neutral, or
ii. if the vehicle is an automatic, in park.
Operation of the vehicle while testing
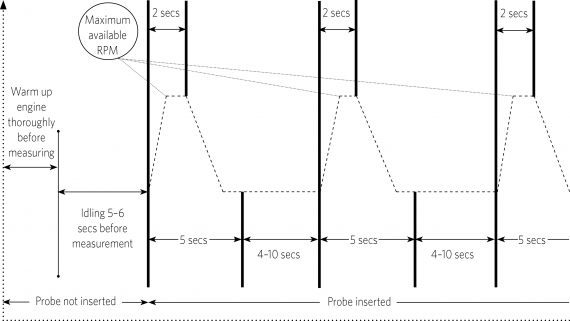
During the test procedure, the vehicle operation cycle must follow these phases (refer to Figure 11-3-1):
1. Purge
a) Residual smoke must be purged from the vehicle’s exhaust system before the vehicle’s diesel smoke is sampled.
2. Inserting probe
a) The probe (the exhaust gas sampling part of the measuring equipment) must be inserted sufficiently into the exhaust pipe to prevent outside air from entering the probe and ensure that only exhaust gas is sampled.
3. Idling before testing
a) The engine must be run at idle for five or six seconds before the first test cycle.
4. Test cycle
a) The accelerator pedal must be fully and rapidly depressed, held in this state for two seconds, then released for three seconds (refer to Figure 11-3-2).
b) Despite the above, if the opacimeter has a function allowing the measurement of the engine revloutions per minute (RPM), the accelerator pedal should only be depressed until the maximum available RPM is indicated by the opacimeter (rather than for the fixed period of two seconds).
c) The exhaust emissions must be sampled throughout this (five-second) period.
5. Idling between test cycles
a) The engine must be run at idle for 4–10 seconds between each test cycle that is performed.
Measured values
1. One, two or three test cycles must be performed as necessary.
a) If the result of measurement 1 is:
i. less than or equal to an optical absorption coefficient (OAC) of 0.64m-1, the vehicle passes the test,
ii. more than an OAC of 0.64m-1, the test cycle must be repeated.
b) If the result of measurement 2 is:
i. less than or equal to an OAC of 0.64m-1, the vehicle passes the test,
ii. more than 0.64m-1, the test cycle must be repeated.
c) If the average of the three measurements is:
i. less than or equal to an OAC of 0.80m-1, the vehicle passes the test,
ii more than an OAC of 0.80m-1, the vehicle fails the test.
2. To avoid doubt, if the vehicle does not meet the prescribed standard after three test cycles, the vehicle fails the test.
Figure 11-3-1. Diesel exhaust emission test vehicle operation cycle using an opacimeter
Procedure for measuring exhaust emissions of diesel vehicles (using filter paper test equipment)
Pre-testing
1. The test equipment must be warmed up and calibrated before use, in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Insert the sampling probe (ie the exhaust gas sampling part of the measuring equipment) far enough into the exhaust pipe to prevent the admission of open air. This is to ensure that only exhaust gas is sampled.
Operation of the vehicle during testing
For the duration of the test:
a) the vehicle must be stationary, and
b) the handbrake must be applied, and
c) the vehicle’s transmission must be:
i. in neutral, or
ii. if the vehicle is an automatic, in park.
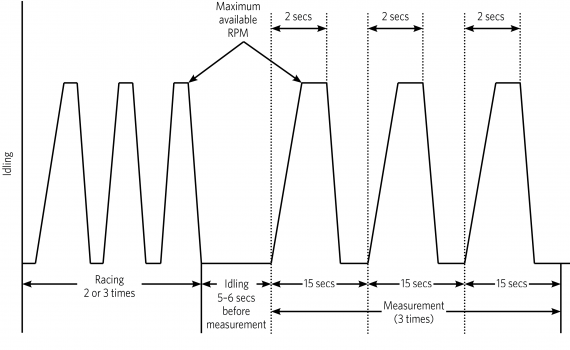
During the test procedure, the vehicle operation cycle must follow these phases (refer to Figure 11-3-2 over the page):
1. Racing purge
a) When the engine is idling, rapidly depress the accelerator to the maximum available RPM.
b) Immediately after the engine reaches its maximum available RPM, release the accelerator to return the engine to idling.
c) Repeat this two more times.
2. Idling phase
a) Run the engine at idle for five or six seconds.
3. Measuring phase
a) Fully depress the accelerator and hold for two seconds.
b) Release the accelerator for 13 seconds and sample the diesel smoke during this period.
c) Repeat this two more times.
Diesel sampling requirements
1. A sample of 0.33 litres must be absorbed through a filter paper by means of a pump-type exhaust smoke sampling device.
2. Class 5A filter paper (or equivalent) must be used.
3. The extent the filter paper is polluted by the smoke contained in the vehicle’s exhaust emissions must be measured by a prescribed exhaust smoke analyser measurement device.
4. The final result must be calculated as an average of the three measured values obtained during the test procedure.
Pass requirements
A diesel vehicle must not exceed 25% opacity.
Figure 11-3-2 Diesel exhaust emission test vehicle operation cycle
Page amended 1 January 2013 (see amendment details).