Correct as at 15th April 2024. It may be superseded at any time.
Extract taken: from Vehicle Inspection Portal > VIRMs > In-service certification (WoF and CoF) > Motorcycles > Lighting > Headlamps
4-1 Headlamps
Reasons for rejection
Mandatory and permitted equipment
1. A motorcycle is not fitted with one dipped-beam headlamp.
2. A motorcycle is fitted with more than:
a) two dipped-beam headlamps, or
b) two main-beam headlamps.
3. A motorcycle (eg a vintage or veteran motorcycle) does not meet standard headlamp requirements, and:
a) does not have a valid vehicle identity card with a lighting equipment endorsement, or
b) does not meet the conditions of the lighting equipment endorsement in its vehicle identity card.
4. A device that allows the headlamps to flash alternately is fitted to a motorcycle that is not an emergency vehicle or a pilot vehicle.
5. A motorcycle is fitted with a dipped-beam headlamp that projects the maximum intensity of the beam to the right.
Condition (Note 4)
6. A lamp is insecure, obscured, or contains moisture in the form of large droplets, runs or puddles .
7. A lens is missing, or has a hole, crack or other damage that allows moisture or dirt to enter.
8. A reflector is damaged or has deteriorated so that light output is reduced.
9. A main-beam headlamp warning device is obscured from the driver’s vision.
Performance
10. When switched on, a headlamp emits light that is:
a) not substantially white or amber, or
b) not approximately equal in colour or intensity from the other lamp in a pair, or
c) not steady, or
d) not bright enough to illuminate the road ahead, eg due to modification, deterioration or an incorrect light source, or
e) too bright, eg due to the fitment of an HID or LED conversion kit (Note 7) or other incorrect light source (see also reason for rejection 16 below), or
f) altered, eg due to damage or modification.
11. When the dipped-beam headlamps are switched on (with wheels pointing straight ahead):
a) a lamp does not operate, or
b) more than the two lamps operate on dipped beam, or
c) more than four lamps operate on dipped beam on a motorcycle first registered anywhere between 1 January 1977 and 31 March 1980, or
d) the light beam produces an incorrect beam pattern, is not focused, or is reduced or altered, or
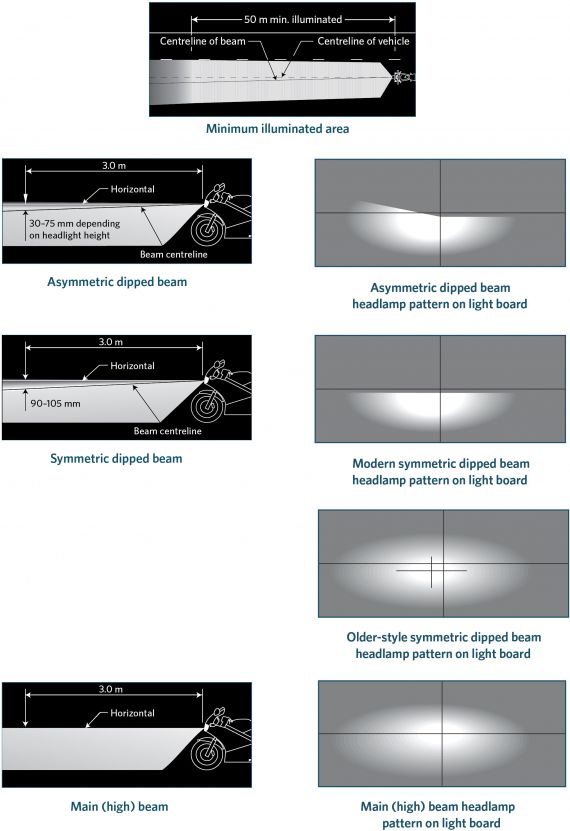
e) the centreline of the light beam is too far to the left or slopes down too far so that the headlamp is no longer capable of illuminating the road at least 50m ahead (Figure 4-1-1), or
f) the centreline of a lamp’s beam projects to the right of the motorcycle’s centreline, or projects down from the lamp at an angle other than:
i. as specified by the motorcycle or lamp manufacturer, or
ii. as specified in Table 4-1-1.
12. When the main-beam headlamps are switched on (with wheels pointing straight ahead):
a) a lamp does not operate, or
b) more than two lamps operate on main beam, or
c) the centreline of a lamp’s beam projects to the right of the motorcycle’s centreline or up from the horizontal, or
d) the lightbeam produces an incorrect beam pattern, is not focused, or is reduced or altered, or
e) the lamps are not capable of being switched to dipped beam or switched off from the driver’s seating position, or
f) a main-beam headlamp warning device does not indicate to the driver that the main-beam headlamps are switched on.
13. A device fitted to a motorcycle that allows the headlamps to flash alternately:
a) does not indicate to the driver that the device is activated, or
b) flashes:
i. faster than two flashes per second, or
ii. slower than one flash per second, or
iii. at a varying frequency.
14. Where a headlamp comprises an array of light sources (eg LEDs) fewer than 75% of these operate.
Modifications
15. An overlay has been applied that reduces or distorts the light emitted from the lamp (eg a tinted cover).
16. A headlamp is retrofitted with a type of light source other than that specified by the vehicle manufacturer or the headlamp manufacturer (eg a headlamp designed for a halogen bulb is fitted with any other type of light source such as an HID or LED bulb, or any other light source such as LED strips or non-OEM angel eyes).
17. A retrofitted pair of headlamps is not fitted:
a) symmetrically, or
b) as far towards each side of the motorcycle as practicable.
18. A retrofitted dipped-beam headlamp is positioned at a height exceeding 1.2m from the ground.
Note 1
If the dipped-beam headlamps are able to be adjusted from the driver’s seating position, the alignment must be checked with the adjustment at its highest position.
Note 2
If the motorcycle is fitted with self-levelling suspension, the alignment must be checked with the suspension at its normal level.
Note 3 Definitions
Headlamp means a lamp designed to illuminate the road ahead of a vehicle, and that is a:
a) dipped-beam headlamp (single lamp), or
b) main-beam (high-beam) headlamp (single lamp), and includes a driving lamp, or
c) combination of a dipped-beam headlamp and a main-beam headlamp (dual lamp unit).
Dipped-beam headlamp means a headlamp that is designed to emit a dipped beam, which is a beam of light that is angled downwards in such a way that it prevents undue dazzle or discomfort to oncoming drivers and other road users.
Main-beam headlamp means a headlamp that is designed to illuminate the road over a long distance ahead of the vehicle.
Modify means to change a vehicle from its original state by altering, substituting, adding or removing a structure, system, component, or equipment, but does not include repair.
Repair means to restore a damaged or worn vehicle, its structure, systems, components or equipment to within safe tolerance of its condition when manufactured, including replacement with undamaged or new structures, systems, components or equipment.
An original equipment (OE) lamp is one that is fitted by the vehicle manufacturer in the original position, or is an equivalent replacement or aftermarket lamp suitable for the position provided by the vehicle manufacturer for that lamp.
All other lamps are considered retrofitted (non-OE).
Note 4
If a headlamp is fitted with a readily removable cover, other than a clear plastic cover, this must be removed for inspection of the headlamp.
Note 5
A vehicle originally manufactured with a headlamp arrangement that differs from what is required or permitted in this section may retain the original headlamps provided they remain fitted in their original position and perform as intended by the vehicle manufacturer.
Note 6
A forward-facing permitted lamp that does not comply with the equipment, condition and performance requirements must be made to comply or be removed from the vehicle.
Note 7
A high-intensity discharge (HID or Xenon HID) or LED conversion kit consists of an HID or LED bulb which fits into the original headlamp unit in place of the original bulb with no change to the headlamp lens, reflector or housing.
It is illegal to fit an HID or LED conversion kit to a vehicle as it brings the headlamp out of standards compliance by producing poor beam patterns and light that is often far too bright to be safe. The bulbs can also produce light that is noticeably blue and not the required substantially white or amber colour. Vehicle and headlamp manufacturers do not permit this modification, and these kits cannot be LVV certified.
It is permitted to replace a complete halogen headlamp unit with a complete HID or LED headlamp unit. If the vehicle is required to meet an approved safety standard for headlamps, only approved headlamps can be retrofitted.
Table 4-1-1. Allowable dipped-beam headlamp alignment
Headlamp type | Distance from ground to centre of light source | Dip rate of beam centre: lower and upper limits | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Percent (%) | mm/3 m | Degrees (°) | |||
EITHER | Any headlamp dipped beam | N/A | That specified by the motorcycle or headlamp manufacturer | ||
OR | Headlamp with and older-style symmetric dipped-beam pattern (see Figure 4-1-2) | N/A | 3.0–3.5 | 90–105 | 1.7–2.0 |
OR | Headlamp with a modern symmetric or asymmetric dipped-beam pattern and distance from ground to centre of light source (see Figure 4-1-2) | less than 0.8m | 1.0–1.5 | 30–45 | 0.57–0.85 |
0.8–1.2m | 1.0–2.0 | 30–60 | 0.57–1.15 | ||
more than 1.2m | 2.0–2.5 | 60–75 | 1.15–1.43 | ||
Table 4-1-2. Dipped-beam angle conversions
Percent (%) | mm/3 m | Degrees (°) | Percent (%) | mm/3 m | Degrees (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1.0 | 30 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 69 | 1.3 | |
1.1 | 33 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 72 | 1.4 | |
1.2 | 36 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 75 | 1.4 | |
1.3 | 39 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 78 | 1.5 | |
1.4 | 42 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 81 | 1.5 | |
1.5 | 45 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 84 | 1.6 | |
1.6 | 48 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 87 | 1.7 | |
1.7 | 51 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 90 | 1.7 | |
1.8 | 54 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 93 | 1.8 | |
1.9 | 57 | 1.1 | 3.2 | 96 | 1.8 | |
2.0 | 60 | 1.1 | 3.3 | 99 | 1.9 | |
2.1 | 63 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 102 | 1.9 | |
2.2 | 66 | 1.3 | 3.5 | 105 | 2.0 |
Figure 4-1-1. Dipped beams
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
- Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Lighting 2004
- New Zealand Gazette, 28 August 1980, issue 108, page 2569.
Mandatory and permitted equipment
1. A motorcycle:
a) must be fitted with one or two dipped-beam headlamps, and
b) may be fitted with one or two main-beam headlamps.
2. A motorcycle (eg a vintage or veteran motorcycle) manufactured without lamps, or with lamps that cannot meet specified requirements, may obtain a WoF if:
a) the motorcycle has a valid vehicle identity card with a lighting equipment endorsement, and
b) the motorcycle meets the conditions of that endorsement.
3. A vehicle required to meet an approved safety standard for lighting must continue to meet an approved safety standard for lighting.
4. A warning device may be fitted that indicates that the main-beam headlamps are switched on.
5. An emergency vehicle or a pilot vehicle may be fitted with a device that allows the headlamps to flash alternately, provided it is also fitted with equipment that indicates to the driver that the device is activated.
6. A retrofitted pair of headlamps must be symmetrically mounted as far towards each side of the motorcycle as ispracticable.
7. A retrofitted dipped-beam headlamp must be positioned at a height not exceeding 1.2 m from the ground.
Prohibited equipment
8. A dipped-beam headlamp designed solely for a left-hand drive vehicle, where the maximum intensity of the beam is dispersed to the right, must not be fitted.
Condition
9. A headlamp must:
a) be in sound condition, and
b) not be obscured.
Performance
10. A headlamp must operate in a way that is appropriate for the lamp and the vehicle.
11. A headlamp must emit a steady light.
12. A headlamp must provide sufficient illumination and light output to illuminate the road ahead.
13. If fitted with a device that allows headlamps to flash alternately, the lamps must flash at a fixed frequency.
14. A pair of headlamps must emit light that is approximately of equal colour and intensity when switched on.
15. A headlamp must emit a beam that is substantially white or amber.
16. A main-beam headlamp must be capable of being dipped or turned off from the driver’s position.
17. A warning device that indicates that the main-beam lamps are in operation must be in good working order.
18. When the headlamps are switched on and the motorcycle’s front wheel is pointing in the straight ahead position:
a) the headlamp beam must be either parallel to or to the left of the longitudinal centreline of the motorcycle, and
b) the centre of a main-beam headlamp beam must be either parallel to or dipping down from the horizontal, and
c) the centre of a dipped-beam headlamp beam must dip at an angle specified by the motorcycle or lamp manufacturer, or
i. 3–3.5% for a symmetric beam pattern, or
ii. 1–1.5% for an asymmetric beam pattern where the centre of the light source is less than 0.8m from the ground, or
iii. 1–2% for an asymmetric beam pattern where the centre of the light source is 0.8–1.2m from the ground, or
iv. 2–2.5% for an asymmetric beam pattern where the centre of the light source is above 1.2m from the ground.
19. The dipped beam headlamps must illuminate the road ahead for 50m in normal darkness.
20. A device fitted to a motorcycle that allows the headlamps to flash must:
a) make the headlamps flash alternately at a frequency of 1–2 Hertz, and
b) incorporate equipment that indicates to the driver that the device is activated.
21. A headlamp must be fitted with a light source that is specified by the motorcycle manufacturer or the headlamp manufacturer.
22. Where a headlamp comprises an array of light sources (eg LEDs), at least 75% of these must operate.
Modifications
23. A headlamp that is affected by a modification must meet equipment, condition and performance requirements.
Page amended 1 April 2021 (see amendment details).