Correct as at 9th May 2024. It may be superseded at any time.
Extract taken from: Vehicle Inspection Portal > VIRMs > In-service certification (WoF and CoF) > Heavy PSVs > Miscellaneous items
13 Miscellaneous items
13-1 Engine and transmission
Reasons for rejection
Mandatory equipment
1. The engine compartment is not lined with, or made of, fire-resistant materials.
Condition and performance
2. Refer to heavy vehicle pages.
3. Fuel, oil or other combustible materials have accumulated or dripped on to a high temperature surface within the engine compartment.
4. A fire-resistant lining is:
a) missing, or
b) damaged or deteriorated so that the risk of fire is increased.
Modification
5. Refer to heavy vehicle pages.
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Mandatory equipment
1. The engine compartment must be lined with, or made of, fire-resistant materials, in a manner that complies with the engine manufacturer's specifications for minimum clearances.
Permitted equipment
2. The vehicle may be fitted with a device to restrict the field of swing of a driveshaft in the event of driveshaft failure.
Condition and performance
3. Refer to heavy vehicle pages.
4. The design of the engine installation and engine compartment must ensure that no fuel, oil or other combustible materials could accumulate in the engine compartment or drip onto any high temperature surface.
5. The engine compartment of a heavy PSV, with an engine positioned rearward of the front axle set must be maintained:
a) free of any build-up of residual fuel, oil or other combustible material, and
b) to ensure that the clearance space between the lining or compartment walls and the engine or its ancillary components is maintained within safe tolerance of the clearance that existed when the engine was installed.
6. Devices to protect against driveshaft failure must be maintained within safe tolerance of their original condition.
Modification
7. Refer to heavy vehicle pages.
Page amended 1 October 2012 (see amendment details).
13-2 Fuel system
Reasons for rejection
Mandatory equipment
1. Fuel for a PSV is carried in a temporary fuel tank.
Condition and performance
2. Refer to general vehicle pages.
3. A fuel tank or fuel line shows signs of corrosion.
4. The fuel-tank filling inlet cannot be accessed from outside the body.
5. A fuel cap:
a) does not tighten properly, or
b) seal is in poor condition.
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Mandatory equipment
1. Fuels for a PSV and the vehicle’s equipment must be carried in permanent fuel tanks.
2. Each filling inlet must be provided with a leak-proof cap.
Condition and performance
3. Refer to general vehicle pages.
4. Fuel tanks and fuel lines must be:
a) corrosion resistant, and
b) designed and constructed of durable, fuel-resistant material, and
c) securely mounted, and
d) reasonably protected from collision damage.
5. Access to the fuel-tank filling inlet must be from outside the body of the PSV.
13-3 LPG/CNG fuel system
Reasons for rejection
Mandatory equipment
1. A vehicle that is equipped with an LPG or CNG fuel system that is in working order does not have a current alternative fuel inspection certificate (Note 1) (Note 2) (Figure 13-3-1).
Condition
2. An LPG or CNG fuel system component is:
a) loose, or
b) significantly corroded, distorted or cracked.
3. A gas line:
a) shows signs of corrosion damage (Note 3), such as pitting, or
b) is bulging, or
c) is insecure, or
d) is damaged, eg cut or crimping.
4. There is a noticeable gas leak.
5. There is corrosion damage, distortion or fracture within 300mm of a tank mounting
Note 1 Definitions
Alternative fuel inspection certificate means evidence of vehicle inspection relating to the periodic in-service inspection and certification of an LPG or CNG fuel system.
Alternative fuel installation certificate means an inspection and certification document relating to the installation of an LPG or CNG fuel system. It is not required for the issue of a WoF or CoF.
LPG/CNG fuel system means a fuel storage and conducting system that is used to provide liquid petroleum gas (LPG) or compressed natural gas (CNG) for the purpose of propulsion of a vehicle.
Note 2
An LPG or CNG fuel system with all the necessary components is deemed to be in working order, whether or not it is charged. A system that has had the filler connection removed is deemed to be not in working order.
Note 3
Corrosion damage is where the metal has been eaten away, which is evident by pitting. The outward signs of such corrosion damage is typically displayed by the lifting or bubbling of paint. In extreme cases, the area affected by the corrosion damage will fall out and leave a hole.
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Mandatory equipment
1. A motor vehicle equipped with an LPG or CNG fuel system that is in working order must display a current alternative fuel inspection certificate.
Condition
2. An LPG or CNG fuel system must be in safe working condition.
Modification
3. The installation of an LPG or CNG fuel system is not a modification that requires certification by a LVV specialist certifier.
4. A modification to an existing LPG or CNG fuel system must be inspected and certified by an approved LPG or CNG fuel inspector or inspecting organisation.
13-4 Electrical wiring
Reasons for rejection
Condition and performance
1. An electrical cable is not:
a) insulated and protected from damage that could be caused by water, fuel, oil, other fluids, dirt or heat, or
b) if practicable, clipped or otherwise gathered into looms with an insulated material, or
c) appropriately and securely fastened to the vehicle, or
d) protected from damage where it passes through holes in the vehicle structure.
2. An electrical cable that enters the passenger compartment is not protected by a secure cover.
3. A detachable service cover inside the vehicle giving access to electrical cables or equipment does not have a sign warning of the operating voltage.
4. A heavy PSV with an engine positioned rearward of the front axle set that entered service as a PSV on or after 1 October 2012 does not have:
a) all batteries secured and easily accessible; or
b) battery terminals and leads protected against the risk of a short circuit.
5. An electrical cable or insulation shows signs of overheating, chafing or other damage.
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition
Electrical voltages up to and including 32 volts AC or 115 volts DC:
1. The electrical current ratings appropriate to that make and model of cable as installed in the PSV must not be exceeded.
2. Electrical cables must be:
a) insulated and protected from heat, water, fuel, oil and other fluids used in the PSV, and
b) held securely in position and protected from damage due to cutting, abrasion or chafing.
3. Any cable that enters or passes through the passenger compartment must be protected from damage by secure covers.
4. A heavy PSV with an engine positioned rearward of the front axle set that entered service as a PSV on or after 1 October 2012 must comply with the following requirements:
a) all batteries secured and easily accessible; or
b) battery terminals and leads protected against the risk of a short circuit.
5. Where electrical cables or equipment are installed in a PSV there must be a sign warning of the operating voltage adjacent to any detachable service cover giving access to the electrical cables or equipment.
Page amended 1 October 2012 (see amendment details).
13-5 Electric and hybrid vehicle fuel and electrical system
Reasons for rejection
Condition (Note 1)
1. High voltage wiring is:
a) insecure or not adequately secured
b) damaged or deteriorated (including insulation)
c) likely to touch:
i. hot components of the vehicle
ii. sharp edges
iii. rotating parts
iv. the ground.
2. High voltage batteries are:
a) insecure or not adequately secured
b) damaged or deteriorated (including components and electrical insulation)
c) leaking, or showing signs of leaking.
3. High voltage battery or wiring shields are damaged or not in place.
4. A high voltage component’s (eg battery) coolant system is leaking.
5. An electrical system warning lamp is illuminated. See Table 13-5-2 for examples.
Modification
4. A modification affects the electrical system, and:
a) is not excluded from the requirements for specialist certification (Table 13-5-1), or
b) is missing proof of specialist certification, that is:
i. the vehicle is not fitted with a valid certification plate (eg low volume vehicle plate or heavy vehicle certification plate/label), or
ii. the operator is not able to produce a valid modification declaration or authority card
iii. The vehicle has not been certified to an accepted overseas system as described in Technical bulletin 13.
Note 1
Vehicle inspectors are only required to do a visual check. An invasive check is not required.
Table 13-5-1. Modifications that do not require specialist certification
Fitting of or modification to: | Specialist certification is not required provided that: |
|---|---|
Fuel system changes and modifications |
Note: Specialist certification is always required for changes to the high voltage electrical system. |
| High voltage battery and control systems |
Note: For clarity, ‘similar weight’ is within 30kg of the original battery pack weight. |
Fitting of or modification to: | Specialist certification is never required: |
|---|---|
Any modification for the purposes of law enforcement or the provision of emergency services |
|
Table 13-5-2. Electrical system warning icons
General fault The vehicle may indicate exactly what the fault is. If the fault is not from an electrical system, or other safety critical system (eg brakes, steering, electrics, ESC etc.) the vehicle may pass the inspection. |  |
Vehicle electrical fault The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. If the fault is not from a safety critical system (eg brakes, steering, high voltage electrics, ESC etc.), the vehicle may pass the inspection. |  |
Limited power/Limp mode This is likely to do with a fault in the electric drive system. The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. |  |
Serious electrical fault The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. | 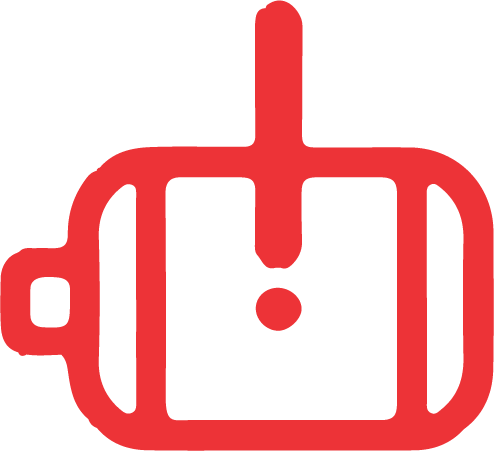 |
Master warning Could be a warning for any vehicle system and is likely to be serious. The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. |  |
High battery temperature Remove the car from any indoor premises immediately and turn the vehicle off. The vehicle should be referred to a repairer for diagnostics. The vehicle must fail the inspection. | 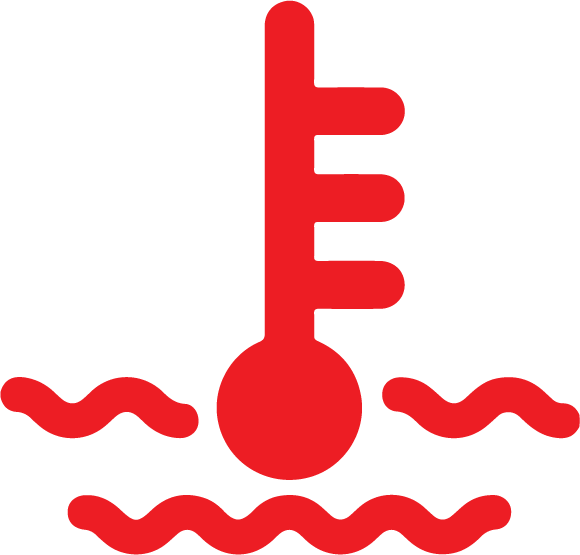 |
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
Condition and performance
1. The vehicle must be safe to be operated.
2. The components and materials must be fit for their purpose and within safe tolerance of their state when manufactured or modified.
Modifications
3. A modification that affects the electrical system must be inspected and certified by an specialist certifier, unless the vehicle:
a) is excluded from the requirement for specialist certification (Table 13-5-1), and
b) has been inspected in accordance with the requirements in this manual, including those for equipment, condition and performance.
Page amended 1 October 2021 (see amendment details).