Correct as at 25th April 2024. It may be superseded at any time.
Extract taken from: Vehicle Inspection Portal > VIRMs > Light vehicle repair certification > Vision
3 Vision
3-1 Windscreen
Reasons for rejection
1. A windscreen that is required to be made of laminated glass is not made of laminated glass.
2. The incorrect adhesive has been used to bond in a piece of glazing.
3. A piece of glazing that is required to comply with an approved glazing standard did not comply, or cannot be demonstrated to have complied, with at least one of the standards listed in Table 3–1–1 at the time the glazing was fitted (Note 3).
4. A windscreen that has been repaired has not been repaired to an approved standard.
5. There is no documentation to support that a repair to a windscreen has been completed to an approved standard.
6. A piece of glazing fitted to a vehicle of class LA, LB1, LB2, LC, LD, LE1 or LE2 is not made of a transparent material that does not shatter.
7. A windscreen has scratches, discolouration or other defects that unreasonably impair the driver’s vision or compromise the strength of the windscreen.
8. The windscreen bonding area of the A-pillar has been repaired and the original glazing adhesive has not been removed fully or until only a thin film is left before the new adhesive was used.
9. The wrong adhesive has been used previously and the original glazing adhesive has not been removed fully before the new adhesive was used.
Note 1
For a vehicle manufactured before 1 January 1991, a glazing marking which contains one or more of the approved trade names in Table 3–1–2 is evidence that a piece of glazing complies with an approved glazing standard.
Note 2
Curved scenic skylights above the cant rail, curved windows at the front and rear corners, skylights, louvres and interior partitions in omnibuses (vehicles of class MD1 and MD2) are not required to comply with approved glazing standards if they are made of transparent material that does not shatter.
Note 3
Any repairs to a windscreen must have documentation to show that the repair was carried out to an approved standard.
Table 3-1-1 List of approved glazing standards*
|
UN-ECE Regulation No. |
EEC/EC Directive |
FMVSS |
ADR |
Japan |
Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
43 |
92/22 2001/92 |
205 |
8 |
TS for Window Glass or JIS R3211 |
BS 857 BS 5282 BS AU 178a ANSI/SAE Z26.1 NZS 5443 AS 2080 AS/NZS 2080 SABS 1191/1193 or ABG (behind driver only) |
* A piece of glazing that is required to comply with an approved glazing standard must comply with at least one of the standards listed in the table.
Table 3-1-2. Approved trade names for glazing
| Armourfloat Armourplate Blindex Duolite Safety Duplate Safety Flolite Ford Indestructo Ford Safety Glass Ford Silver Arrow Glacetex |
Hankuk Glass Safety Heat Line HMC Glass Safety Hankuk TF5 HMC Glass Safety Hankuk TV5 Indestructo Nippon Safety NM Laminated Safety Glass FHP Peerless |
Plexite Safetyflex Safety MGB (Meloplate) Safety MGB (Melite Safety Plate) Sekurit Sigla Spectrofloat Splintex Sunmat Suntex Safety Glass |
Temperlite Temperlite Santa Marina Thorex Connex Triplex Triplex Plate Tuflite Tyneside Veracetex |
Table 3-1-3. Glossary of codes for safety glass (including laminated glass) (Note 1)
|
L |
laminated glass |
|
F |
float glass |
|
P |
plate glass |
|
LF |
laminated float |
|
LP |
laminated plate |
|
/ |
toughened, when near the |
|
// or /// |
laminated, when near the |
|
TS |
toughened glass |
|
TP |
toughened plate |
|
T |
toughened or tempered |
|
Z |
zone tempered |
|
HP |
high performance laminated safety glass |
|
WHP |
complies with impact test (windscreen high performance laminated safety glass) |
|
DOT |
Department of Transport (USA) |
|
AS AS |
the glass, in the direction of the arrow, complies with the 70% light transmission requirement |
|
ANSI |
American National Standards Institute |
|
FMVSS codes |
|
|
AS1 |
for use anywhere in the vehicle |
|
AS2 |
for use anywhere in the vehicle other than windscreen |
|
AS3 |
for rear and rear side windows only |
|
AS4 and AS5 |
for glazing not used for driver’s vision (eg the rear window of heavy truck cabs or convertible tops, windows/doors in motorhome bodies, ute canopies, rear windows on buses, roof glazing etc) |
|
Glazing cut from mother sheet |
|
|
L.76WHP |
laminated, 0.76 mm interlayer, suitable for all locations |
|
L.38 |
laminated, 0.38 mm interlayer, must not be used for windscreens |
|
PCZ26.1 |
polycarbonate, meets requirements of ANSI Z26, must not be used for windscreens |
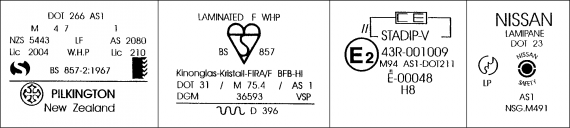
Figure 3-1-1. Approved standards markings
The above standard markings may assist in determining compliance with approved standards.
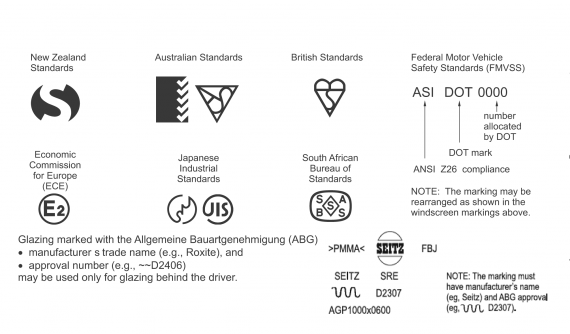
Figure 3-1-2. Typical laminated glazing markings
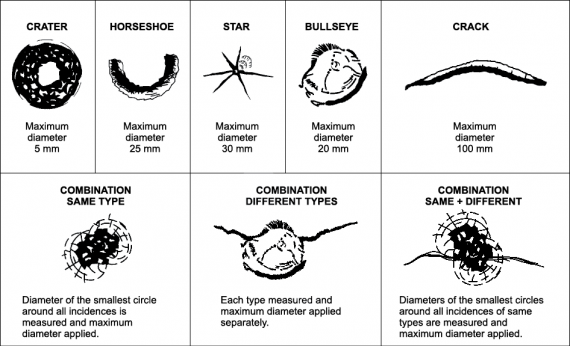
Figure 3-1-3. Types and maximum sizes of windscreen damage
Summary of legislation
Applicable legislation
- Land Transport Rule: Vehicle Repair 1998
- Land Transport Rule: Glazing, Windscreen Wipe and Wash, and Mirrors 1999.
Mandatory equipment
1. Windscreens fitted to the following vehicles must be made of laminated glass:
a) vehicles of class MA, MB, MC and NA manufactured on or after 1 July 1986
b) vehicles of class MD1 and MD2 manufactured on or after 1 July 1997
c) vehicles not covered by any of the defined vehicle classes manufactured on or after 1 January 2001.
2. All glazing fitted to vehicles of class LA, LB1, LB2, LC, LD, LE1 and LE2 must be made of a transparent material that does not shatter.
Compliance with approved standards
3. Windscreens fitted to the following vehicles must comply with one or more of the approved glazing standards in Table 3–1–1:
a) vehicles of group M and N manufactured on or after 1 January 1960, and
b) vehicles not covered by any of the defined vehicle classes manufactured on or after 1 January 2001.
4. Glazing in locations other than windscreens fitted to the following vehicles must comply with one or more of the approved glazing standards in Table 3–1–1:
a) vehicles of group M (Note 2) and N manufactured on or after 1 February 1977 (Note 1)
b) vehicles not covered by any of the defined vehicle classes manufactured on or after 1 January 2001.
Condition
5. A windscreen must be mechanically sound, strong and securely affixed to the vehicle.
6. A windscreen must not have scratches or other defects that:
a) unreasonably impair vision, or
b) compromise its strength.
Page amended 1 October 2013 (see amendment details).